🟢 View File Extensions and Hidden Files/Folders¶
File Extensions¶
File extensions are suffixes added to the end of a file name, usually consisting of a period (dot) followed by a few characters.
File extensions indicate the file's format or type.
Common file extensions include:
.py(Python files).ipynb(Jupyter Notebook files).csv(Comma-separated value files).md(Markdown files)
Understanding file extensions is essential for identifying file types and working with project files.
Hidden Files and Folders¶
Some files and folders are hidden by default to prevent accidental modification or deletion.
These hidden items often contain system configuration or project settings.
In data analytics projects, we need to see these.
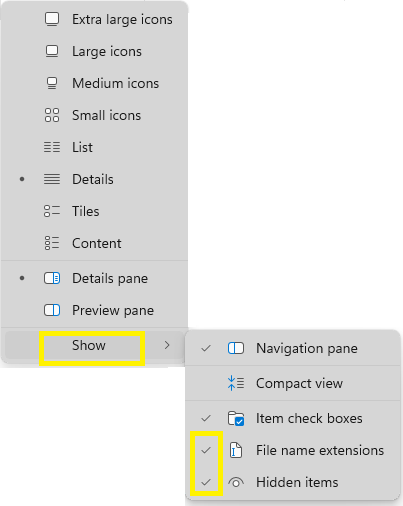
Task 1. Enable View Settings¶
On Windows:¶
- Open File Explorer.
- Click the View tab.
- In the Show group, check:
- File name extensions
- Hidden items
On Mac:¶
- Open Finder.
- Toggle hidden files and folders:
- Press
Cmd+Shift+.(dot) - Enable file extensions:
- In Finder, go to Finder > Settings > Advanced
- Check Show all filename extensions

On Linux:¶
- Open your file manager.
- Enable viewing hidden files and folders:
- Use the file manager's settings or menu option to show hidden files.
- Enable viewing file extensions:
- Use the file manager's settings to display file extensions.
Verify¶
Open a folder and check that file names end with extensions
(for example .txt or .py) and that hidden files are visible.